728x90
ApiApplication
package com.bx.api;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class ApiApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiApplication.class, args);
}
}application.properties
# RabbitMQ (RK3588 IP)
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.0.24
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
spring.rabbitmq.password=passwordTopic의 핵심: 와일드카드(Wildcards)
Topic 방식의 가장 큰 특징은 **점(.)**으로 구분된 라우팅 키와 두 가지 특수 기호를 사용할 수 있다는 점입니다.
- * (별표): 정확히 단어 하나를 대체합니다. (예: *.orange.*)
- # (우물 정): 0개 이상의 단어를 대체합니다. (예: lazy.#)
RabbitTopicConfig
Spring Boot에서 Topic 방식을 쓰려면 TopicExchange와 Binding을 설정
package com.bx.api.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitTopicConfig {
// 1. Topic 타입의 Exchange 생성
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange("log.exchange");
}
// 2. 큐 생성
@Bean
public Queue errorQueue() {
return new Queue("error.queue");
}
// 3. 바인딩 (에러 로그만 이 큐로 오게 설정)
@Bean
public Binding bindingError(Queue errorQueue, TopicExchange topicExchange) {
// "#.error" 패턴을 가진 메시지만 errorQueue로 연결
return BindingBuilder.bind(errorQueue).to(topicExchange).with("#.error");
}
@Bean
public MessageConverter jsonMessageConverter() {
// 이 설정이 있어야 객체 <-> JSON 변환이 가능합니다.
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}TopicConfig
Topic 방식은 Exchange, Queue, Binding 정의
package com.bx.api.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class TopicConfig {
public static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "log.topic.exchange";
public static final String ALL_LOG_QUEUE = "all.log.queue";
public static final String ERROR_LOG_QUEUE = "error.log.queue";
// 1. Topic Exchange 선언
@Bean
public TopicExchange logExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(EXCHANGE_NAME);
}
// 2. 큐 선언 (모든 로그용 / 에러 전용)
@Bean
public Queue allLogQueue() {
return new Queue(ALL_LOG_QUEUE);
}
@Bean
public Queue errorLogQueue() {
return new Queue(ERROR_LOG_QUEUE);
}
// 3. 바인딩 (와일드카드 사용)
@Bean
public Binding bindAll(Queue allLogQueue, TopicExchange logExchange) {
// "seoul.#" -> 서울에서 발생하는 모든 로그(info, warn, error 등) 수집
return BindingBuilder.bind(allLogQueue).to(logExchange).with("seoul.#");
}
@Bean
public Binding bindError(Queue errorLogQueue, TopicExchange logExchange) {
// "#.error" -> 지역 상관없이 모든 에러 로그만 수집
return BindingBuilder.bind(errorLogQueue).to(logExchange).with("#.error");
}
}메시지 보내기 (Producer) : LogProducer
package com.bx.api.service;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.bx.api.config.TopicConfig;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogProducer {
private final RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendLog(String location, String level, String message) {
// 라우팅 키 생성 예: "seoul.info" 또는 "busan.error"
String routingKey = location + "." + level;
Map<String, String> logData = new HashMap<>();
logData.put("location", location);
logData.put("level", level);
logData.put("message", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(TopicConfig.EXCHANGE_NAME, routingKey, logData);
System.out.println("Sent Log with Key [" + routingKey + "]: " + message);
}
}메시지 받기 (Consumer) : LogConsumer
package com.bx.api.service;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.bx.api.config.TopicConfig;
@Service
public class LogConsumer {
// 서울 지역의 모든 로그 처리
@RabbitListener(queues = TopicConfig.ALL_LOG_QUEUE)
public void consumeAllSeoulLog(Map<String, String> message) {
System.out.println("[서울 통합 관제센터] 수신: " + message);
}
// 전 지역의 에러 로그만 처리
@RabbitListener(queues = TopicConfig.ERROR_LOG_QUEUE)
public void consumeErrorLog(Map<String, String> message) {
System.out.println("[긴급 에러 알람] 수신: " + message);
}
}로그 메시지 전송용 Controller 구현
package com.bx.api.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.bx.api.service.LogProducer;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RabbitController {
private final LogProducer logProducer;
/**
* HTTP GET 호출을 받아 RabbitMQ로 메시지 전송 실행 주소:
* http://localhost:8080/send?loc=seoul&lvl=info&msg=test_message
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
public Map<String, Object> sendMessage(@RequestParam(value = "loc") String location,
@RequestParam(value = "lvl") String level, @RequestParam(value = "msg") String message) {
// 이전에 만든 Producer의 메서드 호출
logProducer.sendLog(location, level, message);
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("status", "success");
result.put("routingKey", location + "." + level);
result.put("payload", message);
return result;
}
}실행
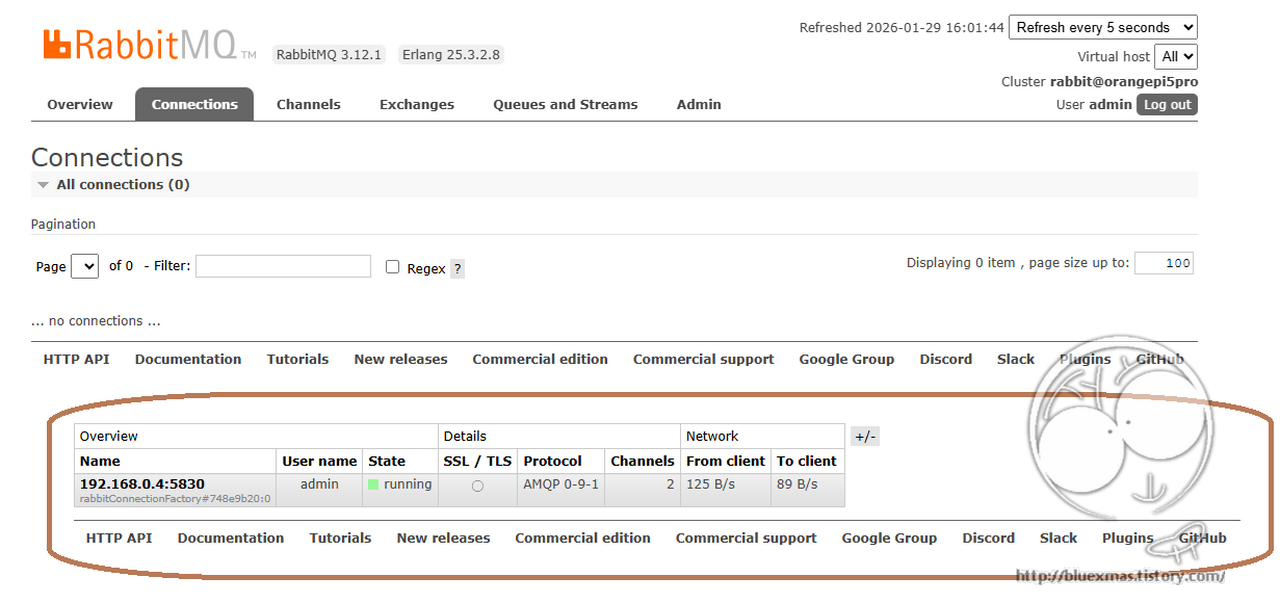


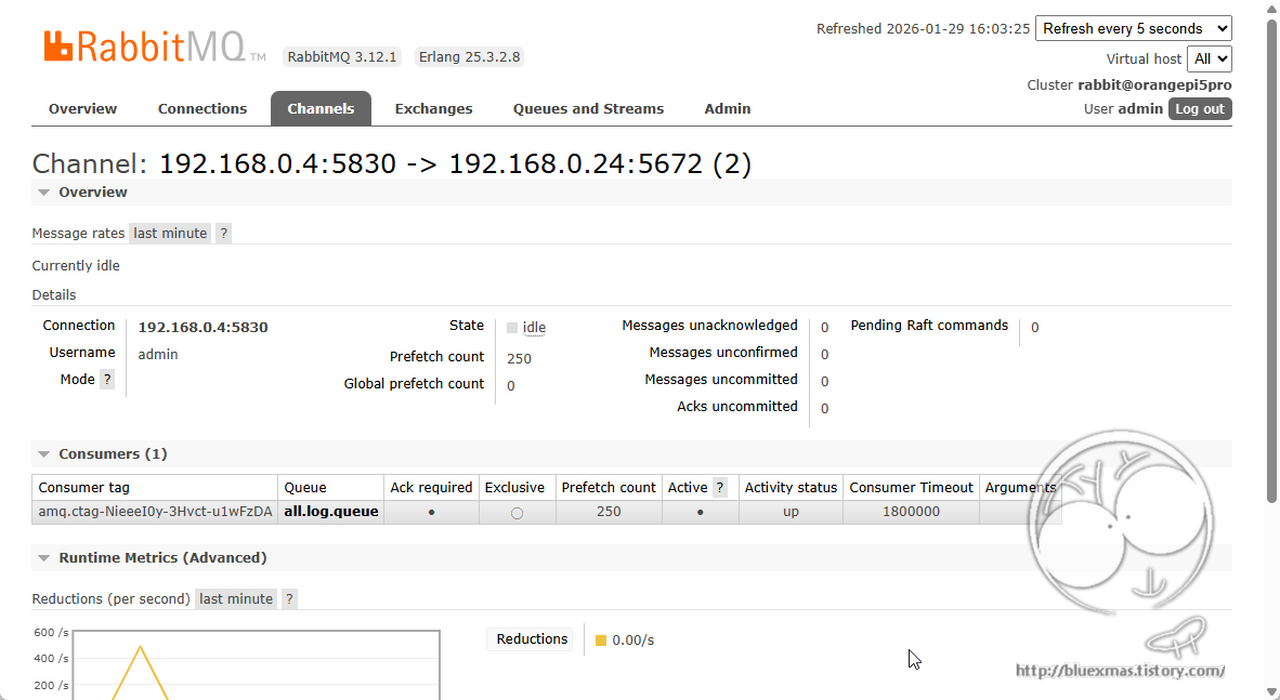
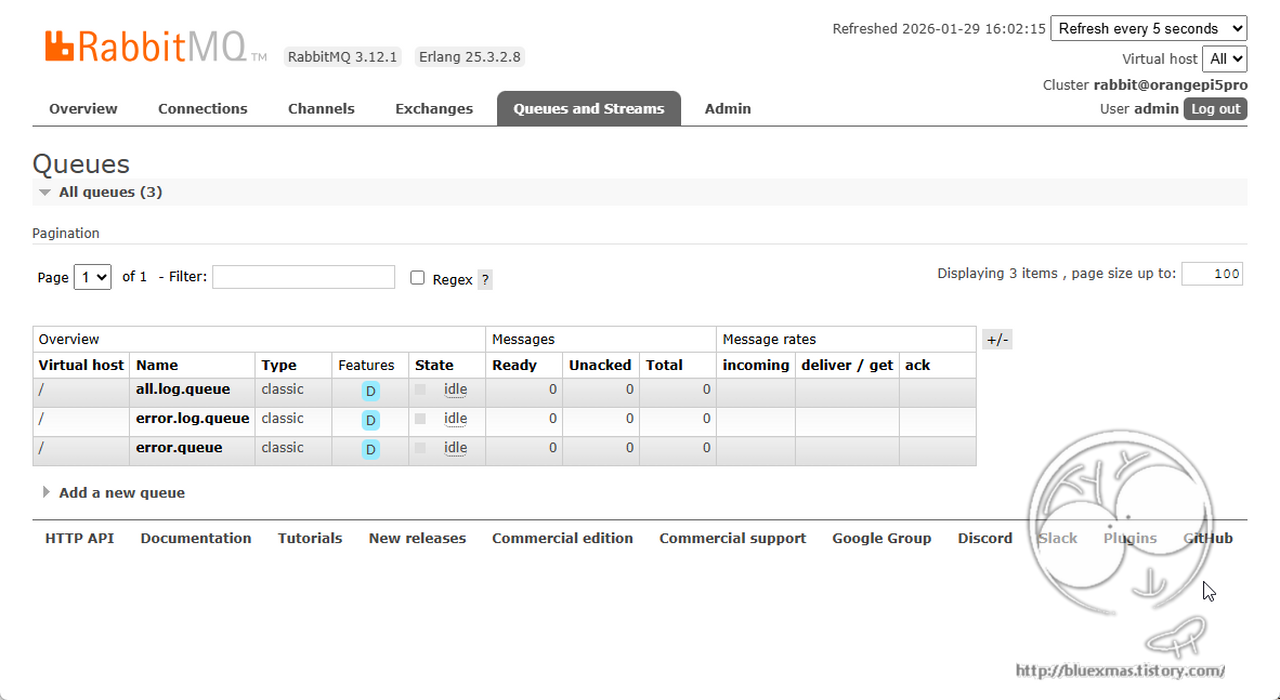
메시지 전송
호출 주소 예제
http://192.168.0.4:8080/send?loc=seoul&lvl=info&msg=test_message서버 로그
Sent Log with Key [seoul.info]: test_message
[서울 통합 관제센터] 수신: {level=info, location=seoul, message=test_message}728x90